AirFlow Openshift Cluster Boilerplate
This boilerplate provides an Airflow Cluster using Kubernetes Executor hosted in Openshift.
Setup
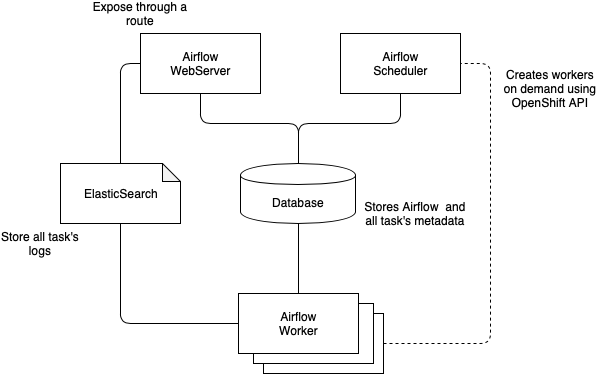
The AirFlow Cluster setup that is provided is based on the KubernetesExecutor and will create and destroy worker pods on demand. It also setup an ElasticSearch instance as the log repository for all workers. As illustrated bellow:
All Airflow images are based on shared-service/airflow image stream. All documentation can be found at
https://github.com/opendevstack/ods-core/tree/master/shared-images/airflow
To deploy the quickstarter the component name must be airflow-worker otherwise nothing will be created
Contents
These are the OpenShift resources and the repository structure created by
this boilerplace. Nothing will be created if any rersouces in the target
OpenShift namespace can be found under the label cluster=airflow
OpenShift Resources
This boilerplate create several resources in OpenShift and ALL of them
can be found using the label cluster=airflow. The created resources are:
-
Service Account:
-
airflow: Service account used as OAuth client for the Airflow web server
-
-
Secrets:
-
airflow-postgresql: Credentials for the PostgreSQL database -
airflow-elasticsearch: Credentials for the ElasticSearch -
airflow-fernetkey: Fernet key for securing stored Airflow Connection
-
-
Config Maps:
-
airflow-environemnt: Airflow configuration shared among all nodes
-
-
Builds and Image Stream:
-
airflow-worker: Worker image which Airflow uses for executing the tasks
-
-
Deployment Configs and Services:
-
airflow-webserver: Airflow Web Server -
airflow-scheduler: Airflow Scheduler (* Only Deployment Config) -
airflow-postgresql: Airflow matadata database -
airflow-elasticsearch: Worker log database -
airflow-kibana: Interface for exploring Airflow logs in ElasticSearch
-
-
Routes:
-
airflow-webserver: Exposes Airflow webserver
-
File structure provided in the repository
. ├── docker │ ├── scripts │ │ └── setup.py # Script for installing python dependecies in dag_deps │ └── Dockerfile # Docker file pointing to Airflow shared image ├── src # Source folder │ ├── dag_deps # Folder containing all dependencies of the DAGs │ │ └── dag_deps_package # Example package │ │ ├── __init__.py │ │ └── crazy_python.py │ ├── dags # All DAGs should be in this folder │ │ ├── hello_dag.py # Example DAG using BASH Operator │ │ ├── hello_kubernetes_operator.py # Example DAG using Kubernetes Operator │ │ └── hello_python_dag.py # Example DAG using internal and external dependencies │ └── requirements.txt # File defining all dependencies (with an example inside) ├── tests # Test source folder │ ├── dag_deps # Folder containing tests of dependecies │ │ ├── __init__.py │ │ └── test_crazy_python.py # Test example │ └── dags # Folder containing tests of DAGs │ ├── __init__.py │ └── test_dag_integrity.py # DAG integrity test ├── Jenkinsfile ├── build.sh # Build script ├── sonar-project.properties ├── test_all.sh # Script for running all tests └── test_dag_integrity.sh # Script for running DAG integrity tests
Features
Multi Branching
An Airflow cluster will be created in each environment. This allows the DAG development to follow the same branching strategy adopted in the whole project
Configuration of Airflow
The configuration of all deployments is documented in https://github.com/opendevstack/ods-core/tree/master/shared-images/airflow